Ethercat ESI 文件
这个主要是在学习 ethercat igh 过程中的一个记录,不算是教程,如果对你有帮助也挺好.
前沿
1 |
详细的建议参考 ETG2000_S_R_V1i0i10_EtherCATSlaveInformationSpecification.pdf
也最好有这个文档,因为能查详细的数据. 因为学习嘛,主要学习先用到的。
EtherCATInfo
1 | <EtherCATInfo xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="EtherCATInfo.xsd" Version="1.6"> |
| Element | Data Type | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Version | xs:string | O | EtherCAT device description schema version used as schema for this device description file. |
| EtherCAT 设备描述模式版本用作此设备描述文件的模式。 |
子节点
| Element | Data Type | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| InfoReference | xs:string | O | File name of an external file based on EtherCATModule.xsd which describes Modules |
| 基于 EtherCATModule.xsd 的外部文件的文件名,该文件描述了模块 | |||
| Vendor | VendorType | M | Describes the identity of the device vendor with its name and EtherCAT Vendor ID assigned by the EtherCAT Technology Group |
| 描述设备供应商的身份,以及由 EtherCAT 技术组分配的名称和 EtherCAT 供应商 ID | |||
| Descriptions | -- | M | Describes the EtherCAT device(s) using the elements Groups, Devices and Modules |
| 描述使用组、设备和模块元素的 EtherCAT 设备。 |
EtherCATInfo 元素是 EtherCAT 从设备描述的根元素
Vendor
主要就是厂商信息:Vendor ID、名称、联系信息等
1 | <Vendor> |
应该还会有其他的,但是主要关注的其实是Id,这个很多是需要的。
1 | EtherCATInfo |
这个 info 一般是不包含的,这个数据是 AI 给我的,见到过这么多 ESI 文件从来没有包含过,当然里面信息也不太重要。
| Element | Data Type | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| FileVersion | xs:int | O | Version of the EtherCAT Slave Information (ESI) file. This version is vendor specific and is not evaluated by the configuration tool. NOTE: Do not confuse FileVersion with the schema version! |
| EtherCAT 从站信息 (ESI) 文件的版本。此版本特定于供应商,不由配置工具评估。 注意:不要将 FileVersion 与架构版本混淆! |
Descriptions
核心定义区(Groups + Devices)
就是核心描述区域
| Element | Data Type | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Groups | -- | M | Similar devices can be assigned to one group. The structuring of devices to groups is used by a configuration tool. The element Groups may define one or several groups with e.g. name and a bitmap symbol. The assignment of a device to a group is made within the element Device:Group. |
| 可以将类似的设备分配给一个组。配置工具使用设备到组的结构。 元素组可以定义一个或多个组,例如 name 和位图符号。 将设备分配给组是在元素 Device:Group 中进行的。 |
|||
| Devices | -- | M | Element Devices may describe one or several devices with their EtherCAT features such as SyncManagers, FMMUs, and Dictionary. |
| Element Devices 可以描述一个或多个具有其 EtherCAT 功能(例如 SyncManagers、FMMU 和 Dictionary)的设备。 | |||
| Modules | -- | O | Element Modules describes all possible modules that can be configured for a modular or complex device. This is typically, but not exclusively, used for devices supporting the Modular Device Profile (ETG.5001) |
| 元素模块描述了可以为模块化或复杂设备配置的所有可能模块。这通常(但不限于)用于支持模块化设备配置文件 (ETG.5001) 的设备 |
Groups
配置工具使用组中设备的结构将设备分组在一起。没有连接到 Groups 元素的从属功能。
他的子节点是 Group
| Element | Data Type | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Group | GroupType | O | One Group groups similar devices with slightly different features. |
| 一个组对功能略有不同的类似设备进行分组。 |
他的作用就是给后续的Device进行分类,我那一个典型的
1 | <Groups> |
Group 的属性
| Element | Data Type | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| SortOrder | xs:int | O | Helps to display multiple groups in the order intended by the vendor. Groups are sorted in ascending order of this value. |
| 有助于按供应商预期的顺序显示多个组。 组按此值的升序排序。 |
|||
| ParentGroup | xs:string | O | Contains string of any Group:Type this entry is subordinated. Improves clearness when list of devices is shown in a configuration tool. Only root groups are allowed (two levels: root, level 1). Parent group shall be defined in the same ESI file as child group. |
| 包含任何 Group:Type 的字符串,此条目是从属的。提高配置工具中显示设备列表时的清晰度。只允许根组(两个级别:根,级别 1)。父组应与子组在同一个 ESI 文件中定义。 |
Type 类型,你可以理解为 Group 的唯一标识
然后在 Device 中,就会有
1 | <GroupType>ServoDrive</GroupType> |
这样就可以进行关联。
Name 名称, 关联之后就会有名称对吧。
这样理论上 **ESI **导入软件就会让你选择分组,选择设备,例如 TwinCAT、Acontis、SOEM GUI 等等软件.
如果你不需要做这的解析其实是不需要关注这个的。
Devices
Devices 元素的组成方式。它描述了运行设备所需的所有设置和功能。
子元素
| Element | Data Type | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Device | DeviceType | O | Holds all information about the device like SyncManager and FMMU, object dictionary, data types and the PDO mapping and assign description. |
| 保存有关设备的所有信息,如 SyncManager 和 FMMU、对象字典、数据类型和 PDO 映射并分配描述。 |
Device 的属性
| Element | Data Type | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Invisible | xs:boolean | O | D: Mandatory for devices which have no EtherCAT functionality (no ESC), e.g. power supply device. Allowed values: ‘0’: EtherCAT slave (has EtherCAT Slave Controller (ESC)) ‘1’: No EtherCAT slave (i.e. not ESC). The device is shown by hardware configuration tools, but is not represented with data within the master configuration file. |
| OD:对于没有 EtherCAT 功能(没有 ESC)的设备(例如电源设备)是强制性的。 允许的值: ‘0’:EtherCAT 从机(具有 EtherCAT 从机控制器 (ESC)) ‘1’:无 EtherCAT 从机(即不是 ESC)。设备按硬件显示 配置工具,但不会在主配置文件中以数据表示。 |
|||
| Physics | PhysicsType | M | Physics at individual ports |
| 各个端口的物理特性 | |||
| Crc32 | HexDecValue | O | CRC Checksum used to check device description against alteration. Refer to 4.2. |
| CRC 校验和用于检查设备描述是否有更改。请参阅 4.2。 |
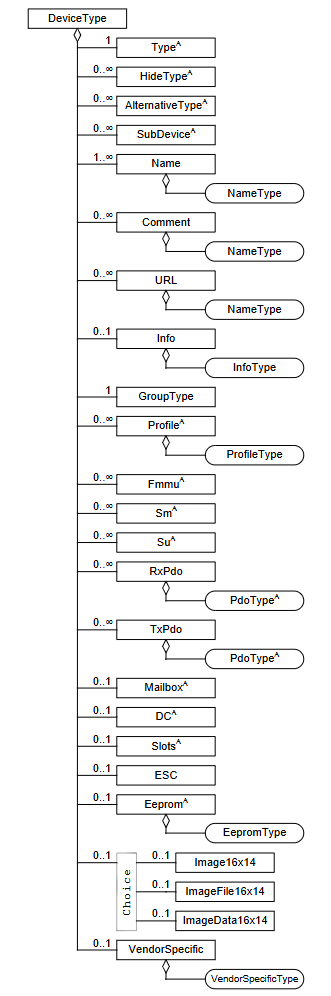
DeviceType
他的属性非常多,所有我会找一些常用的来说,具体的看文档吧
type
| Element | Data Type | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | xs:string | M | Device identity incl. name, product code, revision no |
| 设备标识,包括名称、产品代码、修订号 |
他的属性很重要
1 | <Type ProductCode="#x2406" RevisionNo="143">EYOU_ServoModule_V143</Type> |
也很多属性.
| Element | Data Type | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| ProductCode | HexDecValue | O | Vendor specific product code. Used for identification in conjunction with Vendor ID. (CoE object 0x1018.2) NOTE: The combination of product code and revision number should be unique for one device description and has to match the product code and revision number stored in the EEPROM. |
| 供应商特定的产品代码。与供应商 ID 一起用于标识(CoE 对象 0x1018.2) 注意: 对于一个设备描述,产品代码和修订号的组合应该是唯一的,并且必须与存储在 EEPROM 中的产品代码和修订号相匹配。 |
|||
| RevisionNo | HexDecValue | O | Vendor specific revision number (CoE object 0x1018.3) |
| 供应商特定修订号(CoE 对象 0x1018.3) | |||
| SerialNo | HexDecValue | O | Vendor specific serial number (CoE object 0x1018.4) NOTE: All device with same combination of ProductCode and RevisionNo have same serial number: write serial number to element DeviceType:Type@SerialNo Devices with same combination of ProductCode and RevisionNo have different serial number: SerialNo shall not be used. In this case a serial number shall be written to the SII |
还有很多其他属性, 简单看了下,不常用先不学,后续要用到再说
主要就是这几个属性, 他决定了我们该用哪个Device,因为可能一个ESI文件是对应很多个设备的。
| 参数 | 用于 ESI 匹配 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| Vendor ID | ✅ 是 | 识别设备厂商 |
| Product Code | ✅ 是 | 识别产品型号 |
| Revision No | ✅ 是 | 识别固件/硬件版本 |
| Serial No | ❌ 否 | 区分同型号设备、定位、追踪 |
那先获取信息
1 | === Master 3, Slave 4 === |
这个时候去对应
1 | <Vendor> |
8f 是16进制,转成10进制就是 143
那么我们就找到了对应的
这个就是 type 的作用, 后续我重新做那个软件的时候,就应该这样做
Name,Comment,URL
这里稍微说一下NameType,就是他们的共同属性属性, 数字类型 integer.
可以设置区域代码
1 | <Name LcId="1033">EYOU_ServoModule_ECAT_V143</Name> |
其他用处暂时没有。一般只是显示一个信息。如果要做解析的话,读一下即可.
Info
有关设备的其他信息(ESC 的硬件功能、超时)
InfoType 描述了 EtherCAT 从控制器、状态机和邮箱超时的硬件细节。
这个是一个常用描述, 因为属性过多
1 | <Info> |
| Element | Data Type | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| StateMachine | -- | O | Describes implemented behavior and attributes of the device’s EtherCAT state machine |
| 描述设备的 EtherCAT 状态机的实现行为和属性。 | |||
| StateMachine:Timeout | -- | O | Timeout values describe in milliseconds how long the master waits for the confirmation of a requested state change. The value measures from the time of sending the state change request until the state change is confirmed the latest |
| 超时值以毫秒为单位描述主服务器等待确认请求的状态更改的时间。该值从发送状态更改请求到确认状态更改为止进行度量。 | |||
| StateMachine:Timeout:PreopTimeout | xs:int | M | Timeout time for state transition from INIT → PREOP/BOOT Default value: 3000ms |
| 从 INIT → PREOP/BOOT 状态转换的超时时间默认值:3000ms | |||
| StateMachine:Timeout:SafeopOpTimout | xs:int | Timeout time for state transition from SAFEOP → OP PREOP → SAFEOP Default value: 10000ms |
|
| 从 SAFEOP → OP PREOP → SAFEOP 状态转换的超时时间默认值:10000ms | |||
| StateMachine:Timeout:BackToInitTimeout | xs:int | Timeout time for state transition from OP/SAFEOP/PREOP/BOOT → INIT SAFEOP → PREOP Default value: 5000ms |
|
| 从 OP/SAFEOP/PREOP/BOOT → INIT SAFEOP → PREOP 状态转换的超时时间默认值:5000ms | |||
| StateMachine:Timeout:BackToSafeopTimeout | xs:int | Timeout time for state transition from OP → SAFEOP Default value: 200ms |
|
| 从 OP → SAFEOP 状态转换的超时时间默认值:200ms | |||
| StateMachine:Behavior | -- | State to which the master sets the slave at start up |
|
| 主设备在启动时将从设备设置为的状态 |
另外一个是MailBox的超时。
我拿到的ESI文件中主要就是超时。唯一一个是
1 | <VendorSpecific> |
这个是 VendorSpecificTy 是供应商特定的类型,文章上直接写的any.
GroupType
Reference to a group (described in element Groups) to which this device should be assigned to.
Name of the handle used in element Groups:Group:Type
对应将此设备分配给的组(在元素组中描述)的引用。元素中使用的句柄名称 Groups:Group:Type
这个是前讲过
1 | <GroupType>ServoDrive</GroupType> |
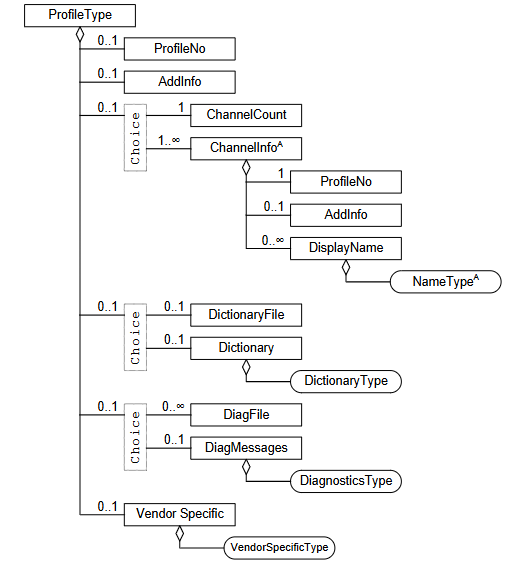
Profile
很重要的东西。
Description of the used profile and object dictionary including data type definition
使用的配置文件和对象字典的描述,包括数据类型定义。
主要是2个东西。
1 | <Profile> |
这个告诉你他的协议,比如我用的基本都是 CIA402 的
首先确认这个对不对。
另外一个就是字典
不用一个一个去读他
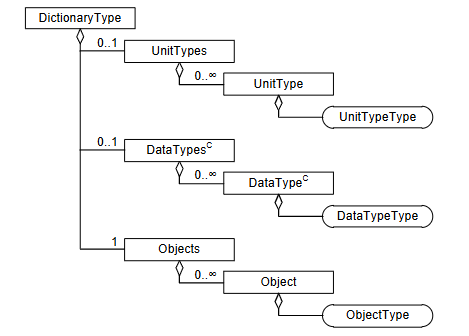
UnitTypes
1 | <UnitTypes> |
这个一般不用,至少目前没见到过
类型定义
1 | <DataTypes> |
这个是最基础的,他有子索引的概念
1 | <DataType> |
0一般是长度,有多少个子索引。后面的格局定义来即可
需要注意的
BitOffs
Bit address of the SubItem value starting at 0.
NOTE: The bit offset of SubItem 0 shall be 0x00.
For SubItems >0 the bit offset can be chosen without any restriction. Padding bits for alignment do not have to be described explicitly
SubItem 值的位地址从 0 开始。
注意:子项 0 的位偏移应为 0x00。对于子项>0,可以不受任何限制地选择位偏移。不必显式描述用于对齐的填充位。
1 | ┌─────┬─────┬─────┬─────┬─────┬─────┬─────┬─────┬─────┐ |
BitOffs 指定每个 SubItem 从第几位开始。
Flags:Access
读写权限
1 | ‘ro’: readonly (default) |
参数列表
1 | <Objects> |
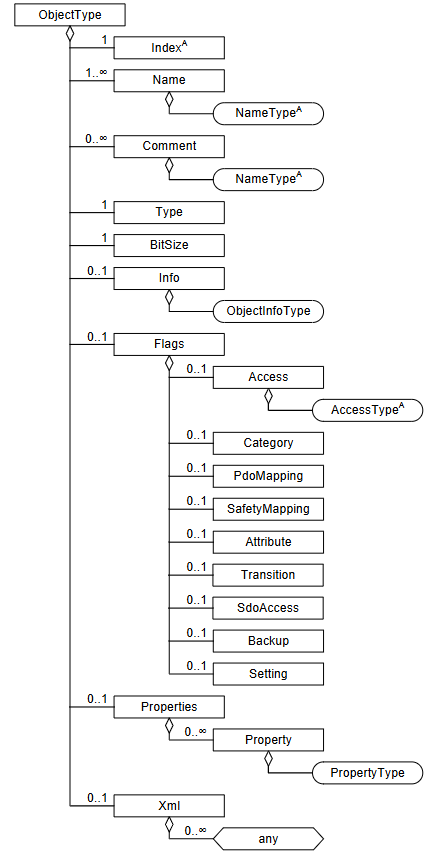
Index 索引
Name 名称
Comment 评论
Type和 BitSize 之类的和 DataType 重复,这个应该需要确认是否有子节点
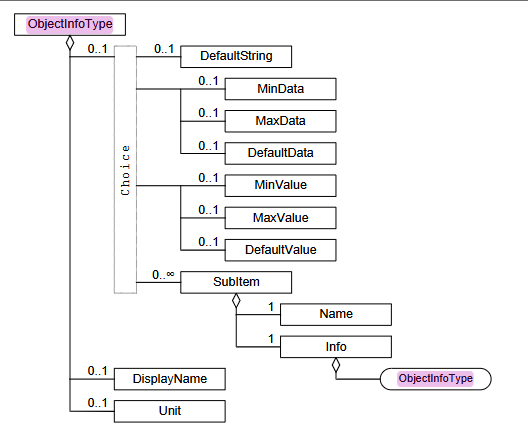
Info 内容说明
这个一般只有一个 DefaultString
他会有一些其他限制
不过目前还没有遇见过其他的
Flags
这个也有很多
1 | <Flags> |
Access
1 | ‘ro’: readonly (default) |
Category
1 | ‘m’: mandatory |
比较重要一点. 得理解这个的含义
| 值 | 全称 | 中文 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|---|
| m | Mandatory | 强制 | 设备必须实现 |
| o | Optional | 可选 | 设备可以不实现 |
| c | Conditional | 条件 | 特定条件下必须实现 |
Fmmu, Sm, Su
他应该是一整个逻辑
1 | [主站侧] |
Fmmu 他的作用是把逻辑地址映射成物理地址
1 | <Fmmu>Outputs</Fmmu> ← FMMU 0:映射输出数据(主→从) |
这个是针对PDO数据
MBoxState FMMU 映射的是”邮箱状态寄存器”,不是邮箱数据本身
Definition of FMMU usage
Allowed values:
‘Outputs’: FMMU is used for RxPDO
‘Inputs’: FMMU is used for TxPDO
‘MBoxState’: FMMU is used to map the Write Event Flag of the
Input Mailbox (register 0x080D.0) to the process data. The Input
Mailbox does not have to be polled by the Master when waiting
for a Mailbox Response. The usage is highly recommended to
reduce traffic.
NOTE: FMMU is always assigned to one process data
SyncManager. If there are n consecutive output SyncManagers
with a physical start address of below 0x1000 and BitSize = 8,
they are all covered by one FMMU with size n*8 bit.
E.g. digital I/O devices without uC.
FMMU 用法的定义 允许的值: ‘Outputs’: FMMU 用于 RxPDO ‘Inputs’: FMMU 用于 TxPDO ‘MBoxState’: FMMU 用于将输入邮箱 (寄存器 0x080D.0) 的写入事件标志映射到进程数据。在等待邮箱响应时,主服务器不必轮询输入邮箱。强烈建议使用以减少流量。
官方文档解释清楚了,现在只需要了解一个概念即可
| Element | Data Type | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| OpOnly | xs:boolean | O | Obsolete configtool: handle like DeviceType:Sm@OpOnly |
| 过时 configtool:像 DeviceType:Sm@OpOnly 一样的句柄 |
|||
| Sm | xs:int | O | D: Mandatory if more than one FMMU for the same direction is used to map data to non-consecutive memory areas Assigns this FMMU to a SyncManager NOTE: SyncManager counting starts with 0 NOTE: If SM assigned for the FMMU it shall match with the SM setting in the PDO |
| 如果同一方向使用多个 FMMU,则必须执行 将数据映射到非连续内存区域将此 FMMU 分配给 SyncManager 注意:SyncManager 计数从 0 开始 注意:如果为 FMMU 分配了 SM,则应与 PDO 中的 SM 设置匹配 |
|||
| Su | xs:int | O | Assigns this FMMU to the related PDO (Pdo@Su) and therefore to a SyncManager |
| 将此 FMMU 分配给相关的 PDO (Pdo@Su),从而分配给 SyncManager。 |
Sm
1 | <Sm MinSize="#x24" MaxSize="#x80" DefaultSize="#x80" StartAddress="#x1000" ControlByte="#x26" Enable="1">MBoxOut</Sm> |
| 通道 | SM名称 | PDO类型 | 数据方向 | 内容示例 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SM0 | MBoxOut | - | 主→从 | SDO 请求 |
| SM1 | MBoxIn | - | 从→主 | SDO 响应 |
| SM2 | Outputs | RxPDO | 主→从 | 控制字、目标位置 |
| SM3 | Inputs | TxPDO | 从→主 | 状态字、实际位置 |
Description of SyncManager including start address and direction.
Allowed values:
‘MBoxOut’: Mailbox Data Master → Slave
‘MBoxIn’: Mailbox Data Slave → Master
‘Outputs’: Process Data Master → Slave
‘Inputs’: Process Data Slave → Master
NOTE: Standard SyncManager assignment as specified in
ETG.1000, part 4 applies.
The first listed SyncManager describes SyncManager0, the
following SyncManager describes SyncManager1, etc.
If more than one SyncManager of same direction and buffer
mode is used attribute Pdo@Su is recommended to make clear
to which Sm a PDO is assigned. If a PDO can be assigned to
different SyncManagers, the attribute should be omitted.
SyncManager 的描述,包括起始地址和方向。允许的值:
‘MBoxOut’:
邮箱数据主站→从站 ‘MBoxIn’:
邮箱数据从站→主站 ‘输出’:
处理数据主站→从站 ‘输入’:
处理数据从站→主站
注意:适用 ETG.1000 第 4 部分中指定的标准 SyncManager 分配。
第一个列出的 SyncManager 描述了 SyncManager0,以下 SyncManager 描述了 SyncManager1,依此类推。如果使用多个相同方向和缓冲区模式的 SyncManager,建议 Pdo@Su 属性以明确将 PDO 分配给哪个 Sm。如果可以将 PDO 分配给不同的 SyncManager,则应省略该属性。
Sm => SyncManager
简单说他就是住站和从站的数据交换机
- 控制逻辑, 管理读写
- 同步状态
- 状态反馈(缓冲区满/空,数据就绪,写保护)
- 保护机制
一系列的。他的属性很多
MinSize: 从站支持的最小 SyncManager 长度(以字节为单位)
MaxSize: 从站支持的最大 SyncManager 长度(以字节为单位)
DefaultSize: 邮箱 SyncManager 进程数据 SyncManager 的必填项:对于进程数据长度,默认 SyncManager 长度是根据元素 RxPDO(用于输出 SyncManager)和 TxPDO(用于输入 SyncManager)中的默认 PDO 分配计算的。SyncManager 的默认大小(以字节为单位)
StartAddress: SyncManager 的强制物理起始地址
ControlByte: 如果 Sm@Virtual = false 则为必填 SyncManager 控制字节(寄存器 0x0804 + y*8;y= SyncManager 数量),包括。SyncManager 模式和方向
这个稍微说一下
| ControlByte 值 | 二进制 | 用途 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0x26 | 0010 0110 | SM0 (MBoxOut) | 邮箱模式+写入+Watchdog |
| 0x22 | 0010 0010 | SM1 (MBoxIn) | 邮箱模式+读取+Watchdog |
| 0x64 | 0110 0100 | SM2 (Outputs) | 三缓冲+写入+Watchdog |
| 0x20 | 0010 0000 | SM3 (Inputs) | 三缓冲+读取+Watchdog |
Enable: 邮箱 SyncManager 必须使用。SyncManager 启用位 (0x0806.0 + y*8) y= SyncManager 允许值数: ‘1’: 启用: SyncManager 活动控制内存 ‘0’: 禁用: SyncManager 没有内存保护 对于邮箱 SyncManagers: 邮箱长度 != 0: 启用 = TRUE 邮箱长度 == 0: 启用 = FALSE 对于进程数据 SyncManagers: 不关心
只用知道是否启用即可。
Su 没怎么见到过.
通过定义由此字符串标识的不同数据报(可能不同的帧)来定义计时上下文。
efines a timing context by defining different datagrams
(possibly different frames) which are identified by this string.
Su = 定义一个”时序上下文”,用于将多个 PDO/SM 分组到同一个 EtherCAT 帧中。
默认情况没有Su的情况,主站会把所有Sm放在同一个组里面
它可以把主站的帧进行分类,比如定义快速和慢速,比如哪些是运动控制之类的。
不过目前没有遇到过
PDO
TxPdo 从=>主
RxPdo 主=>从
和从站通信必须严格按照他的规定来.
他们都属于 PdoType
| Element | Data Type | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Index | HexDecValue | M | PDO index NOTE: RxPDOs: Index area 0x1600 to 0x17FF TxPDOs: Index area 0x1A00 to 0x1BFF |
| PDO 指数 注意:RxPDO:索引区域 0x1600 到 0x17FF TxPDO:索引区域 0x1A00 到 0x1BFF |
|||
| Name | NameType | M | PDO name |
| PDO 名称 | |||
| Exclude | HexDecValue | O | List of PDO indices that are excluded if this PDO is assigned to a SyncManager PDOs are “mutually exclusive” i.e. if a PDO (PDO_A) is excluded by another PDO (PDO_B) than PDO_B also has to be excluded by PDO_A |
| 如果将此 PDO 分配给 SyncManager,则排除的 PDO 索引列表 PDO 是“互斥的”,即如果 PDO (PDO_A) 被另一个 PDO (PDO_B) 排除,则 PDO_B 也必须被 PDO_A 排除。 | |||
| Entry | EntryType | O | Description of all entries according to EntryType |
| 根据 EntryType 描述所有条目 | |||
| ExcludedSm | xs:int | O | SyncManager to which this PDO may not be assigned to. default = PDO can be assigned to all SyncManager with matching type/direction NOTE: When PDO can be assigned to any SM with matching direction and type (1/3-buffer mode) this element is not needed |
| 可能不会将此 PDO 分配给的 SyncManager。默认值 = PDO 可以分配给所有具有匹配类型/方向的 SyncManager |
1 | <Index DependOnSlot="true">#x1600</Index> |
表示冲突,比如我运行 1600 CSP, 就不能运行其他模式.
同时也表示支持其他模式.
ExcludedSm 属于排除。排除一种sm. 暂时不深究, 类似Exclude,也是一种互斥.
主要的还是 EntryType 但是这个也不用多说。就是描述字段
1 | <Entry> |
HexDecValue 这个一直没有关注
以十六进制或十进制格式表示十六进制值,例如 12345 → 12345 (dec) #x12345 → 0x12345 (十六进制),而 0x45 是 LSB 和 0x01 MSB 只允许正值。相应的元素定义中提到了可能的异常。
Represents a hexadecimal value either in hexadecimal or decimal format, e.g.
12345 → 12345 (dec)
#x12345 → 0x12345 (hex), whereas 0x45 is LSB and 0x01 MSB
Only positive values are allowed. Possible exceptions are mentioned in the corresponding
element definition
就是16进制简单这样理解就行了
然后发现了
Index DependOnSlot 这个东西, 他是和 Module 相关的, 当我启用模块,然后在调用的时候, 他会去偏移 DependOnSlot = true 的值
1 | <Slots SlotIndexIncrement="#x800" SlotPdoIncrement="16"> |
这里有两个偏移参数
1 | SlotIndexIncrement="#x800" SlotPdoIncrement="16" |
会让数据偏移, 公式如下
实际 PDO 索引 = 基础索引 + (插槽号 × SlotPdoIncrement)
那么算一下
这个 ESI 只有一个插槽所以他是 0
1 | 1602 + 0 x 16 所以最后就是 1602 |
大概是这样。
DependOnSlotGroup 是插槽号,复杂情况管理起来
MailBox
1 | <Mailbox> |
这里源码中没有属性
DataLinkLayer
‘0’:不支持邮箱数据链路层(无邮箱重复服务)’1’:支持邮箱数据链路层(邮箱重复服务);
注意:根据 ETG.1000.4,对于支持邮箱服务的设备,必须支持邮箱数据链路层(=从丢失的邮箱帧中恢复)。
0’: Mailbox Data Link Layer not supported (no Mailbox repeat service)
1’: Mailbox Data Link Layer supported (Mailbox repeat service);
NOTE: Support of Mailbox Data Link Layer (=recovery from lost
mailbox frame) is mandatory according to ETG.1000.4 for devices
supporting the mailbox service
我目前电机是支持 COE => CANopen over EtherCAT
存在这个条目表示支持 COE,
SdoInfo 是否允许查询字典结构
PdoAssign 是否可以改变SM使用的哪些PDO
PdoConfig 是否可以修改PDO内部的Entry
CompleteAccess 一次读写整个对象
SegmentedSdo 支持分段 SDO, 如果flase 只支持快速SDO
PdoUpload 设备具有动态过程数据,即 PDO 配置和 PDO 分配从设备上传,并根据计算出的 PDO 长度设置 SyncManager 长度。0:取自 ESI 的 PDO 描述,并基于相同的长度计算的 SyncManager 长度
这个时候再来看子节点
Transition
1 | ‘IP’: Init → Pre-Operational |
- ✅ 当设备从 PreOp 转换到 SafeOp 时
- ✅ 自动执行这个 InitCmd(写入 0x6060 = 8)
剩余的Data之类的?
| 0x6060 的值 | 模式名称 | 全称 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | No mode | 无模式 | 未配置 |
| 1 | PP | Profile Position Mode | 位置轨迹模式 |
| 3 | PV | Profile Velocity Mode | 速度轨迹模式 |
| 4 | PT | Profile Torque Mode | 力矩轨迹模式 |
| 6 | HM | Homing Mode | 回零模式 |
| 8 | CSP | Cyclic Sync Position | 循环同步位置 ⭐ |
| 9 | CSV | Cyclic Sync Velocity | 循环同步速度 |
| 10 | CST | Cyclic Sync Torque | 循环同步力矩 |
所以 我这个默认是CSP模式
这个InitCmd 如果没有机必须写
1 | // 主站代码必须写: |
所以我在配置TAISHAN电机的时候
1 | if (ecrt_slave_config_sdo8(sc[i], 0x6060, 0x00, OP_MODE_CSP)) { |
其他的见招拆招吧
Dc
属性
| Attribute | Data Type | Use | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| UnknownFRMW | xs:boolean | O | 0: Slave processes FRMW commands 1: Slave does not process FRMW commands Shall only be TRUE when ESC does not support this command type |
| 0:从机处理 FRMW 命令 1:从机不处理 FRMW 命令 仅当 ESC 不支持此命令类型时,才应为 TRUE。 | |||
| Unknown64Bit | xs:boolean | O | 0: 64 bit time values supported 1: 64 bit time values not supported |
| 0:支持 64 位时间值 1:不支持 64 位时间值 | |||
| ExternalRefClock | xs:boolean | O | 0: DC time of device is not triggered by an external source 1: Device synchronizes to an external clock source (e.g. IEEE1588 clock) |
| 0:设备的直流时间不是由外部源触发的 1:设备同步到外部时钟源(例如 IEEE1588 时钟) | |||
| PotentialReferenceClock | xs:boolean | O | 0: device cannot be used as reference clock 1: device can be used a reference clock (all necessary registers available) NOTE: For devices supporting the necessary DC registers this attribute should be set to 1. Devices supporting any DC mode automatically can be used as reference clock and this attribute may be omitted. |
| 0:设备不能用作参考时钟 1:设备可以用作参考时钟(所有必要的寄存器都可用) 注意:对于支持必要直流寄存器的设备,此属性应设置为 1。自动支持任何直流模式的器件可以用作参考时钟,并且可以省略此属性。 |
|||
| TimeLoopControlOnly | xs:boolean | O | Devices that need the DC SystemTime but not for SYNC/LATCH signals (e.g. bridges), may not support certain registers. The EtherCAT master configures DC (calculate and download Offset value, …) but does not write registers from 0x0940 to 0x09FF (e.g. no Assign/Activate is downloaded) 0: device supports DC with LATCH and/or SYNC unit (default) 1: device uses DC SystemTime but does not support SYNC or LATCH unit. |
| 需要 DC SystemTime 但不需要 SYNC/LATCH 信号的设备(例如网桥)可能不支持某些寄存器。EtherCAT 主站配置直流电(计算和下载偏移值,…)但不将寄存器从 0x0940 写入 0x09FF(例如,未下载分配/激活) 0:设备支持带 LATCH 和/或 SYNC 单元的 DC(默认) 1:设备使用 DC SystemTime,但不支持 SYNC 或 LATCH 单元。 |
这个一般不用了解,因为一般是和我下面这样什么都不写,就意味着全部的DC支持
1 | <Dc> |
接下来子节点
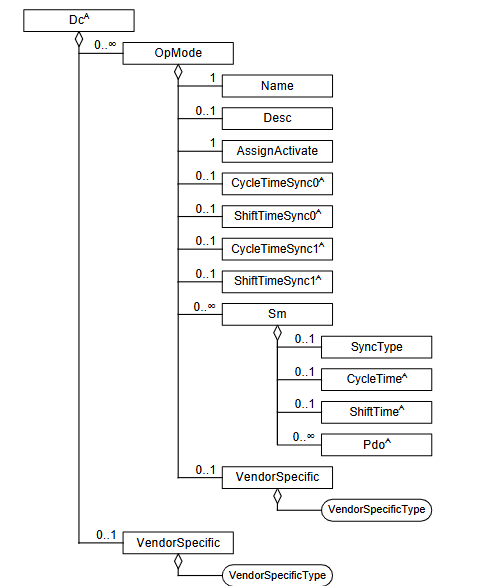
OpMode
支持的作模式的定义(通常是同步的作模式)列出的第一个作模式是默认的。
注意:为了使用 mailbox init 命令定义作模式,使用元素 Device:Slots 和 Modules
Definition of supported operation modes (usuallyoperation modes of synchronization)
The first operation mode listed is the default one.
NOTE: For definition of operation modes with mailbox
init commands the elements Device:Slots and Modules are used
Name 和 Desc 跳过
AssignActivate - DC 同步信号激活寄存器, 控制那些SYNC信号被激活
| 值 | 十进制 | 二进制 | SYNC0 | SYNC1 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #x0 | 0 | 0000 0000 0000 0000 | ❌ 关闭 | ❌ 关闭 | 不使用 DC 同步 |
| #x100 | 256 | 0000 0001 0000 0000 | ✅ 启用 | ❌ 关闭 | 只使用 SYNC0 |
| #x200 | 512 | 0000 0010 0000 0000 | ❌ 关闭 | ✅ 启用 | 只使用 SYNC1 |
| #x300 | 768 | 0000 0011 0000 0000 | ✅ 启用 | ✅ 启用 | 同时使用 SYNC0 和 SYNC1 |
1 | 主站周期(1ms) |
如果启用DC,就只有2种模式
- Sync0
- Sync0 + Sync1
就是一个立刻发出,一个等触发统一发出。
Modules
这个就不赘述了,就是可以模块化
可以在 Devices 使用这个模块,而不用每次都写。